Prompt chaining is a technique used in artificial intelligence, particularly with generative models like large language models (LLMs). It involves creating a sequence of prompts, where the output from one prompt serves as the input for the next. This method allows users to tackle complex tasks more effectively by breaking them down into smaller, manageable components.
Definition and Process
Prompt chaining can be defined as a structured approach to prompt engineering that enhances the performance of AI systems. Instead of issuing a single, comprehensive prompt, users can create a series of prompts that build upon each other. This iterative process helps refine the AI’s outputs and maintain context throughout the interaction. The typical workflow of prompt chaining includes:
- Initial Prompt: The user provides an initial prompt to generate a response.
- Evaluation: The output is assessed for relevance, accuracy, and completeness.
- Follow-Up Prompts: Based on the evaluation, subsequent prompts are crafted to refine or expand upon the initial output.
- Iteration: This cycle continues until the desired quality of response is achieved.
For example, in content creation, a user might first ask the AI to generate an outline for a blog post. After reviewing the outline, the user can issue additional prompts to develop each section in detail, thereby enhancing the final product’s quality and coherence.
Benefits of Prompt Chaining
Prompt chaining offers several advantages:
- Increased Accuracy: By breaking down tasks, users can refine AI responses, leading to more precise outputs.
- Greater Detail: Follow-up prompts allow for deeper exploration of specific topics, resulting in comprehensive responses.
- Improved Control: Users can identify and address gaps in earlier outputs, enhancing overall output quality.
- Scalability: This method allows for easy adjustments and expansions of the task by simply adding new prompts to the chain.
Drawbacks of Prompt Chaining
Despite its benefits, prompt chaining can also present challenges.
- Management Complexity: Coordinating a series of prompts can become complicated, particularly if the chain is lengthy or intricate.
- Dependence on Initial Quality: The effectiveness of the entire chain relies heavily on the quality of the first prompt. A poorly constructed initial prompt can lead to compounded errors in subsequent outputs.
- Time-consuming: Prompt chaining’s iterative nature may require significant time and effort to test and refine each link in the chain.
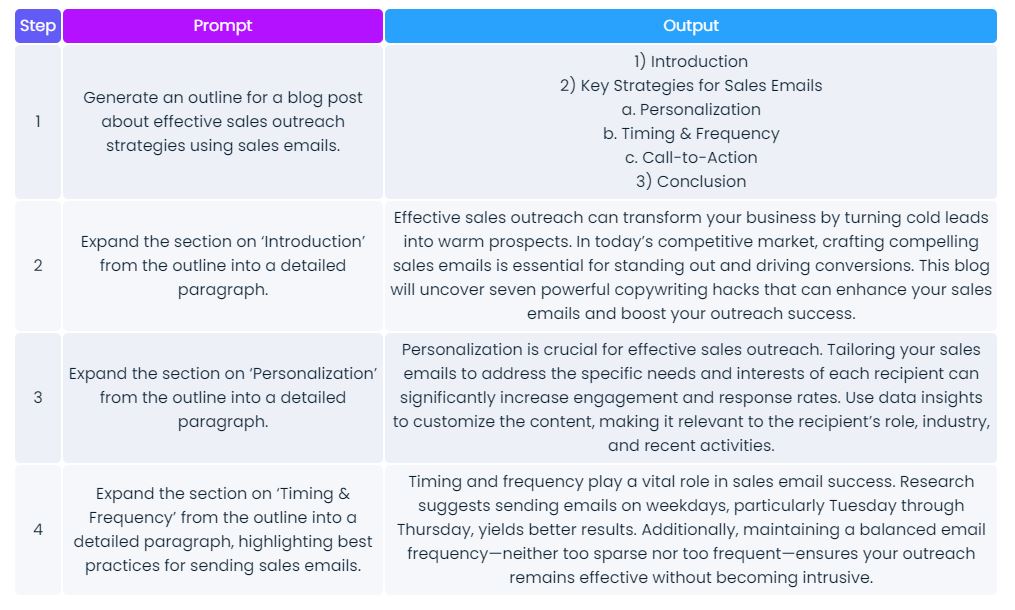
Example of prompt chaining in action
Here’s a simplified example of what a prompt chain sequence might look like;
Use Cases of Prompt Chaining
Prompt chaining is particularly useful in various domains, including:
- Software Development: Developers can use it to generate and refine code iteratively.
- Content Creation: Marketers can create and enhance marketing materials through a structured prompt sequence.
- Strategic Planning: Business leaders can utilize it for detailed scenario analyses and decision-making support.
In summary, prompt chaining is a powerful technique that maximizes the potential of generative AI by providing a structured, iterative approach to solving complex tasks. This method leverages the strengths of large language models (LLMs) to deliver coherent and context-rich outputs, making it an essential tool for businesses across various industries. Ready to unlock the full potential of AI in your marketing strategy? Let Baking AI, the AI marketing agency, help you harness these advanced techniques to drive growth and innovation. Contact us today to learn more!